A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A full census glossary is available from the U.S. Census Bureau here.
Block
See Census block
Block group
A subdivision of a census tract (or, prior to 2000, a block numbering
area), a block group is the smallest geographic unit for which the
Census Bureau tabulates sample data. A block group consists of all
the blocks within a census tract with the same beginning number.
Example: block group 3 consists of all blocks within a 2000 census tract numbering from 3000 to 3999. In 1990, block group 3 consisted of all blocks numbered from 301 to 399Z.
Related Term: Census block, Census tract
CCensus
block
A subdivision of a census tract (or, prior to 2000, a block numbering
area), a block is the smallest geographic unit for which the Census
Bureau tabulates 100-percent data. Many blocks correspond to individual
city blocks bounded by streets, but blocks – especially in
rural areas – may include many square miles and may have some
boundaries that are not streets. The Census Bureau established blocks
covering the entire nation for the first time in 1990. Previous
censuses back to 1940 had blocks established only for part of the
nation. Over 8 million blocks are identified for Census 2000.
Census designated place (CDP)
A statistical entity, defined for each decennial census according to Census Bureau guidelines,
comprising a densely settled concentration of population that is not within an incorporated place,
but is locally identified by a name. CDPs are delineated cooperatively by state and local officials
and the Census Bureau, following Census Bureau guidelines. Beginning with Census 2000 there are no size
limits.
Census tract
A small, relatively permanent statistical subdivision of a county delineated
by a local committee of census data users for the purpose of presenting
data. Census tract boundaries normally follow visible features, but may
follow governmental unit boundaries and other non-visible features in
some instances; they always nest within counties. Designed to be relatively
homogeneous units with respect to population characteristics, economic
status, and living conditions at the time of establishment, census tracts
average about 4,000 inhabitants. They may be split by any sub-county geographic
entity.
Census tract/block
outline maps*
A map showing the census tract and block borders in a county; may be used
to assist in determining the correct identifying number for the desired
area.
Related term: Census tract, Census block, Tract number
Diversity Index Calculation
In terms of calculation, the proportion of population
in a group is multiplied by the natural log of that proportion, e.g.,
50 percent white is calculated as: 0.50 * log(0.50) = -0.3466. In the
special case of a 0.00 proportion, the product of this calculation is
defined as 0.00. These five numbers are then summed and divided by -1.609.
The following example is for the City of Oakland:
| Racial/Ethnic Group | Proportion | Prop*Log(Prop) | Diversity Index |
| White | 0.235 | -0.3403 | |
| Black/Afr Amer | 0.351 | -0.3675 | |
| Asian/Pac Isl | 0.156 | -0.2898 | |
| Hispanic/Latino | 0.219 | -0.3326 | |
| Other | 0.039 | -0.1265 | |
| Total | 1.000 | -1.4567 | 0.905 |
Geographic Information
Systems (GIS)*
A computer system used for storing, integrating,
manipulating, analysing and displaying data related to geographic position.
Typically, a GIS map has several different layers, with each layer holding
data about a particular kind of feature (e.g. roads). Each feature is
linked to a position on the graphical image of a map.
Public Use Microdata Area (PUMA)
An area that defines the extent of territory for which the Census Bureau
tabulates public use microdata sample (PUMS) data.
Public Use Microdata Sample (PUMS)
files
Computerized files containing a small sample of individual records, with
identifying information removed, from the census long form and from the
American Community Survey showing the population and housing characteristics
of the people included on those forms. Provides more detailed data than
other census files, but only for a small sample of the population.
TIGER database
TIGER ® is an acronym for the Topologically Integrated Geographic
Encoding and Referencing (System or database). It is a digital (computer-readable)
geographic database that automates the mapping and related geographic
activities required to support the U.S. Census Bureau’s census
and survey programs. The U.S. Census Bureau developed the TIGER
System to automate the geographic support processes needed to meet
the major geographic needs of the 1990 census: producing the cartographic
products to support data collection and map presentations, providing
the geographic structure for tabulation and dissemination of the
collected statistical data, assigning residential and employer addresses
to the correct geographic location and relating those locations
to the geographic entities used for data tabulation, and so forth.
The content of the TIGER database is undergoing continuous updates
and is made available to the public through a variety of TIGER/Line
® files that may be obtained free of charge from the Internet
or packaged on CD-ROM or DVD from Customer Services, U.S. Census
Bureau, Washington, DC 20233-1900.
Related Term: Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
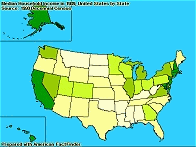
Thematic maps
A map that reveals the geographic patterns in statistical data.
Tract
See Census tract
Tract
numbers
Used to uniquely identify a census tract within a county.
Related Term: Census tract
All definitions © U.S. Census Bureau unless otherwise noted with an asterix (*).
California | Bay Area | Counties | Cities | Tracts/Blocks | Transportation
Historical Data | Maps | Links | FAQ | Home | Contact | MTC | ABAG
MTC-ABAG Library, 375 Beale Street, Suite 800, San Francisco, CA 94105
415-778-5236, library@mtc.ca.gov